 Human Origins
Human Origins
 Paleontology
Paleontology
Fossil Friday: New Evidence for the Human Nature of Neanderthals
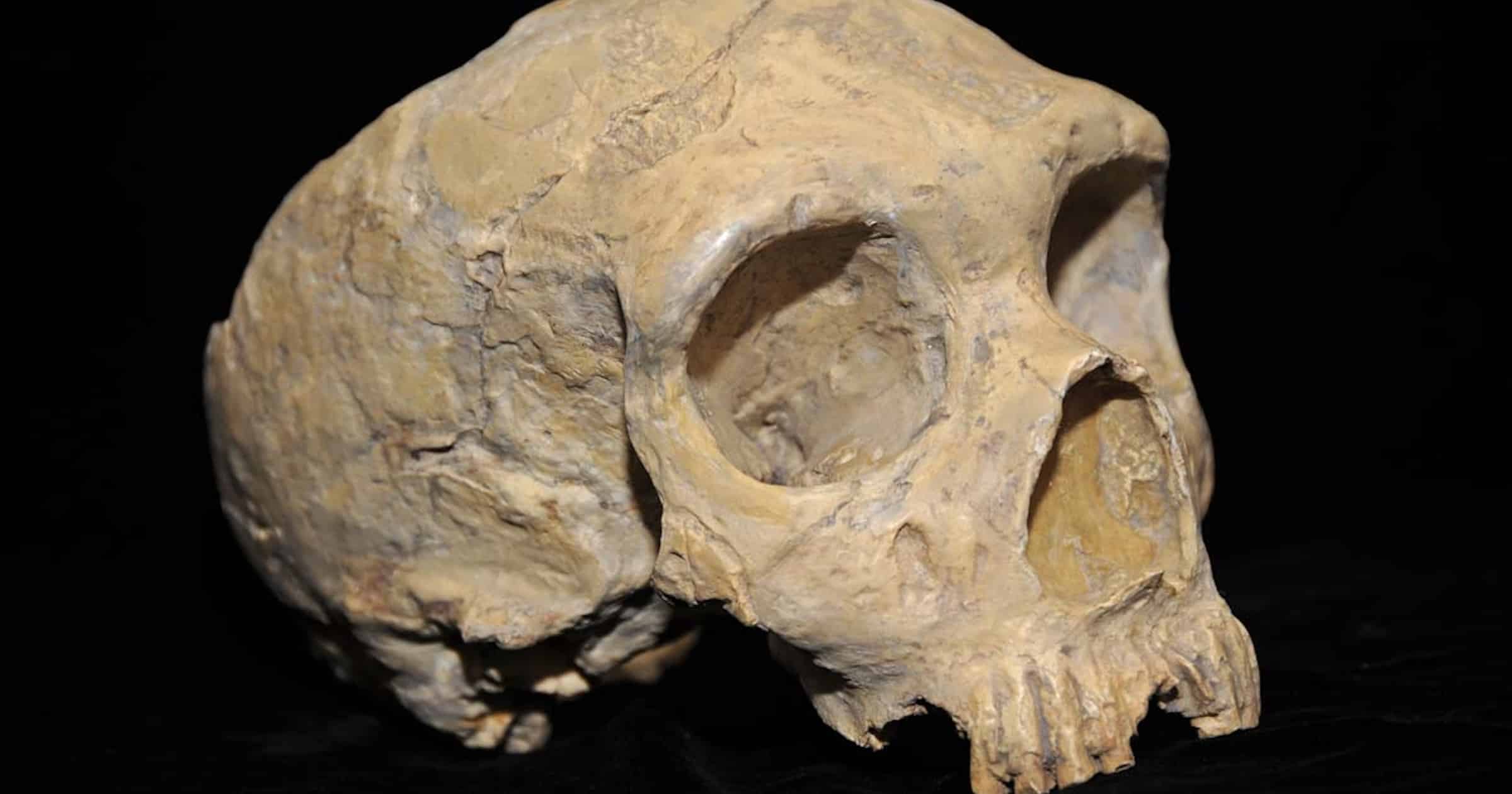
The reconstruction of Neanderthal appearance and behavior has quite a checkered history. After an initial controversy over whether the fossils really represent ancient humans or just malformed modern humans, Neanderthals were described in 1864 as distinct hominin species, Homo neanderthalensis. For a long time they were considered as brutish cavemen with a club and almost gorilla-like appearance. Then the scientific opinion shifted and Neanderthals were more and more recognized as human-like and even as geniuses of the ice age (Husemann 2005, Finlayson 2019), based on an avalanche of new evidence for complex human behavior (Nowell 2023, Vernimmen 2023). We now know that Neanderthals used fire (Angelucci et al. 2023), buried their dead (Balzeau et al. 2020, Dockdrill 2020), created stone circles (Jaubert et al. 2016, Callaway 2016) and bone tools (Soressi et al. 2013), made jewellery from eagle talons (Radovčić et al. 2015, Rodríguez-Hidalgo et al. 2019) and used feathers as body decoration (Peresani et al. 2011, Finlayson et al. 2012), made cave art with paintings and engravings (Rodríguez-Vidal et al. 2014, Hoffmann et al. 2018a, Marquet et al. 2023), played music with bone flutes (Turk et al. 2018), used ochre as pigment (Roebroeks et al. 2012, Hoffmann et al. 2018b) and sophisticated fibre technology (Hardy et al. 2020), produced flour from processed plants (Mariotti Lippi et al. 2023), dived for seafood (Villa et al. 2020), cooked food and self-medicated with herbal painkillers and antibiotics (Hardy et al. 2012, Weyrich et al. 2017), and even produced glue from birch bark with a complex chemical procedure (Blessing & Schmidt 2021, Schmidt et al. 2023).
New Anatomic Data
But it is not just new evidence for Neanderthal behavior that overturned our previous crude image of Neanderthals as dumb brutes, but also new anatomic data. Contrary to earlier beliefs, more recent studies have demonstrated a fully upright posture with typical human spinal curvature called lordosis (Haeusler et al. 2019). The latter authors concluded that ”after more than a century of alternative views, it should be apparent that there is nothing in Neandertal pelvic or vertebral morphology that rejects their possession of spinal curvatures well within the ranges of variation of healthy recent humans.” There even exists compelling new evidence for hearing and speech capacities (Conde-Valverde et al. 2021), which “demonstrates that the Neanderthals possessed a communication system that was as complex and efficient as modern human speech” (Starr 2021).
Correlated with this fundamental rethinking of Neanderthals (Nowell 2023) in terms of their anatomy, culture, and mental capabilities, their classification has also changed over time. At first they were considered as a different species, Homo neanderthalensis, then they were just considered as a subspecies of modern humans, Homo sapiens, and since the late 1990s again as “an unambiguously demarcated morphospecies” (Tattersall & Schwartz 2006; also see Harvati et al. 2004, Márquez et al. 2014, and Wynn et al. 2016). The new field of paleogenomics brought insight into their DNA (Green et al. 2010), which was considered as sufficiently dissimilar to warrant a separate species status again (Clarke 2016), even though there was also evidence for hybridization and genetic admixture with modern humans (Meneganzin & Bernardi 2023). Paleogeneticist and Nobel laureate Svante Pääbo (2014) called the controversy of the species status of Neanderthals as unresolvable, because of the arbitrariness and fuzziness of species concepts (also see Meneganzin & Bernardi 2023, Nowell 2023, and Stringer 2023). The controversy still continues as is evident from a recent article titled “Are Neanderthals and Homo sapiens the same species?” (Heidt 2023), which discusses the fact that “scientists have been vollying the question back and forth for more than a century”. Nowell (2023) wrote: “From their initial discovery until today, Neandertals have shifted between “being recognized as human or being pushed to the constitutive outside of humanness,” what Drell (2000, p. 15) describes as “the oscillating dichotomy of Same and Other.”
Of course, the undeniable evidence for significant and common genetic admixture (Kuhlwilm et al. 2016, Villanea & Schraiber 2019, Callaway 2021), which makes up 1-4 percent of the modern human genome (Reilly et al. 2022), would suggest that Neanderthals and modern humans shared a common gene pool and belonged to the same biospecies. Even the skeptic and ID opponent Michael Shermer (2010) agreed in an article for Scientific American that the genomic evidence suggests that our Neanderthal brethren were not a separate species. Strong reproductive isolation barriers that limited the amount of introgression were proposed by Overmann & Coolidge (2013), but many experts remain unconvinced. Paleoanthropologist Bence Viola from the University of Toronto said (quoted in Vernimmen 2023): “Homo sapiens clearly recognized Neanderthals as mating partners, which suggests they thought of them as humans — maybe ‘the weird guys living behind the mountains,’ but still, fellow humans.”
But what do we make of the anatomical differences between Neanderthals and modern humans? Don’t they support a separate species status? Actually, this would not follow even if the differences lay outside the range of variability of modern humans, because that is also the case in many other subspecies of living animals. However, some human populations such as Australian aboriginals indeed share with archaic humans like Neanderthals a robust skull with pronounced brow ridges, which lead Darwin’s bulldog, Thomas Huxley (in Lyell 1863), to compare them with Neanderthals. Of course this also had some typical Darwinist racist connotations. Just like Neanderthals, native Australians were considered primitive and inferior. Nevertheless, the similarities are real and have been confirmed by modern anatomical studies (e.g., Wolpoff & Caspari 1996), which concluded that “the interpretation of Neanderthals as a different species is very unlikely.” Anatomical and cognitive differences between Neanderthals and anatomically modern humans were also affirmed by Wynn et al. (2016), who nevertheless emphatically rejected labeling these differences as implying inferiority or superiority. More recent research even suggests that the characteristic skull features may rather be based on phenotypic plasticity than an evolutionary heritage from ape-like ancestors (Curnoe 2011).
Why So Much Debate?
So, why is there still so much debate and controversy about the species status of Neanderthals? Well, what is at stake is not just some esoteric species problem in the scientific ivory tower of a few paleoanthropologists, but the very question of human nature and human uniqueness, thus what it even means to be human. The recognition of Neanderthals as a distinct species would make the uncanny valley a bit shallower, as Peeters & Zwart (2020) put it, and would challenge “longstanding ideas about the uniqueness of our species” (Seghers 2018). A so-called multiple species model was proposed for the origin of behavioral modernity (Moro Abadía & González Morales 2010). Even mainstream evolutionary biologists recognize that this is a “politically charged context” (Nowell 2023), and thus certainly subject to bias when you approach this question from either a Darwinist viewpoint of modern materialist and atheist science, or from the Judeo-Christian viewpoint of human exceptionalism, where humans are made in the image of God.
In my humble opinion, the evidence for symbolic thinking, language, and genetic admixture clearly suggests that Neanderthals belong to our very own species. They were no inhabitants of the uncanny valley of objects that just resemble humans (think of Sophia the robot or CGI characters), but they are fully human and should again be classified as Homo sapiens neanderthalensis. The latest technical literature shows that such a view is well rooted in up-to-date mainstream science. McCrae (2023) concluded, in an article titled “Neanderthals might not be the separate species we always thought,” that even though “it’s unlikely we’ll finally see the classification of Homo neanderthalensis fade into obscurity any time soon. … Still, as more sibling than cousin, it seems the poor old Neanderthal deserves to sit right by our side in the Homo sapien[s] family portrait.”
References
- Angelucci DE, Nabais M & Zilhão 2023. Formation processes, fire use, and patterns of human occupation across the Middle Palaeolithic (MIS 5a-5b) of Gruta da Oliveira (Almonda karst system, Torres Novas, Portugal). PLoS ONE 18(10): e0292075, 1–51. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0292075
- Balzeau A, Turq A, Talamo S et al. 2020. Pluridisciplinary evidence for burial for the La Ferrassie 8 Neandertal child. Scientific Reports 10: 21230, 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77611-z
- Blessing MA & Schmidt P 2021. On the efficiency of Palaeolithic birch tar making. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports 38: 103096, 1–5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2021.103096
- Callaway E 2016. Neanderthals built cave structures — and no one knows why. Nature News May 25, 2016. https://www.nature.com/articles/nature.2016.19975
- Callaway E 2021. Oldest Human DNA Reveals Recent Neanderthal Mixing. Nature 592, 339. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-00916-0
- Clarke JLA 2016. Neanderthals: Species or Subspecies? Diversipede 2(1), 24–31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.29173/comp47
- Conde-Valverde M, Martínez I, Quam RM et al. 2021. Neanderthals and Homo sapiens had similar auditory and speech capacities. Nature Ecology & Evolution 5(5), 609–615. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-021-01391-6
- Curnoe D 2011. A 150-Year Conundrum: Cranial Robusticity and Its Bearing on the Origin of Aboriginal Australians. International Journal of Evolutionary Biology 2011: 632484, 1–18. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/632484
- Dockdrill P 2020. Child’s Bones Buried 40,000 Years Ago Solve a Longstanding Neanderthal Mystery. ScienceAlert December 10, 2020. https://www.sciencealert.com/ancient-neanderthal-mystery-solved-by-a-child-s-bones-from-40-000-years-ago
- Finlayson C 2019. The smart Neanderthal. Oxford University Press, Oxford (UK), 240 pp. https://global.oup.com/academic/product/the-smart-neanderthal-9780198797524
- Finlayson C, Brown K, Blasco R et al. 2012. Birds of a Feather: Neanderthal Exploitation of Raptors and Corvids. PLoS ONE 7(9): e45927, 1–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045927
- Green RE, Krause J, Briggs AW et al. 2010. A Draft Sequence of the Neandertal Genome. Science 328(5979), 710–722. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1188021
- Hardy K, Buckley S, Collins MJ et al. 2012. Neanderthal medics? Evidence for food, cooking, and medicinal plants entrapped in dental calculus. Naturwissenschaften 99, 617–626. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-012-0942-0
- Hardy BL, Moncel M-H, Kerfant C, Lebon M, Bellot-Gurlet L & Mélard N 2020. Direct evidence of Neanderthal fibre technology and its cognitive and behavioral implications. Scientific Reports 10: 4889, 1–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61839-w
- Haeusler M, Trinkaus E, Fornai C & Frater N 2019. Morphology, pathology, and the vertebral posture of the La Chapelle-aux-Saints Neandertal. PNAS 116(11), 4923–4927. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820745116
- Harvati K, Frost SR & McNulty KP 2004. Neanderthal taxonomy reconsidered: Implications of 3D primate models of intra- and interspecific differences. PNAS 101(5), 1147–1152. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308085100
- Heidt A 2023. Are Neanderthals and Homo sapiens the same species? LiveScience December 23, 2023. https://www.livescience.com/archaeology/are-neanderthals-and-homo-sapiens-the-same-species?
- Hoffmann DL, Standish CD, Garciá-Diez M et al. 2018a. U-Th dating of carbonate crusts reveals Neandertal origin of Iberian cave art. Science 359(6378), 912–915. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aap7778
- Hoffmann DL, Angelucci DE, Villaverde V, Zapata J & Zilhão J 2018b. Symbolic use of marine shells and mineral pigments by Iberian Neandertals 115,000 years ago. Science Advances 4(2): eaar5255, 1–6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar5255
- Husemann D 2005. Die Neandertaler. Genies der Eiszeit. Campus Verlag, Frankfurt a.M. (DE), 263 pp. [In German]
- Jaubert J, Verheyden S, Genty D et al. 2016. Early Neanderthal constructions deep in Bruniquel Cave in southwestern France. Nature 534, 111–114. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18291
- Kuhlwilm M, Gronau I, Hubisz M et al. 2016. Ancient gene flow from early modern humans into Eastern Neanderthals. Nature 530, 429–433. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16544
- Lyell C 1863. The Antiquity of Man. Dent and Sons, London (UK), 518 pp.
- Mariotti Lippi M, Aranguren B, Arrighi S et al. 2023. New evidence of plant food processing in Italy before 40ka. Quaternary Science Reviews 312(6236): 108161, 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2023.108161
- Marquet J-C, Freiesleben TH, Thomsen KJ et al. 2023. The earliest unambiguous Neanderthal engravings on cave walls: La Roche-Cotard, Loire Valley, France. PLoS ONE 18(6): e0286568, 1–53. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286568
- Márquez S, Pagano AS, Delson E, Lawson W & Laitman JT 2014. The Nasal Complex of Neanderthals: An Entry Portal to their Place in Human Ancestry. The Anatomical Record 297: 2121–2137. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.23040
- McCrae M 2023. Neanderthals Might Not Be The Separate Species We Always Thought. ScienceAlert October 22, 2023. https://www.sciencealert.com/neanderthals-might-not-be-the-separate-species-we-always-thought
- Meneganzin A & Bernardi M 2023. Were Neanderthals and Homo sapiens ‘good species’? Quaternary Science Reviews 303: 107975, 1–11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2023.107975
- Moro Abadía O & González Morales MR 2010. Redefining Neanderthals and art: an alternative interpretation of the multiple species model for the origin of behavioural modernity. Oxford Journal of Archaeology 29(3), 229–243. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0092.2010.00346.x
- Nowell A 2023. Rethinking Neandertals. Annual Reviews of Anthropology 52, 151–170. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-anthro-052621-024752
- Overmann KA & Coolidge FL 2013. Human species and mating systems: Neandertal– Homo sapiens reproductive isolation and the archaeological and fossil records. Journal of Anthropological Sciences 91, 91–110. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24344097/
- Pääbo S 2014. Neanderthal Man: In Search of Lost Genomes. Basic Books, New York (NY), p. 237.
- Peeters S & Zwart H 2020. Neanderthals as familiar strangers and the human spark: how the “golden years” of Neanderthal research reopen the question of human uniqueness. History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences 42: 33, 1–26. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40656-020-00327-w
- Peresani M, Fiore I, Gala M, Romandini M & Tagliacozzo A 2011. Late Neandertals and the intentional removal of feathers as evidenced from bird bone taphonomy at Fumane Cave 44 ky B.P., Italy. PNAS 108(10), 3888–3893. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1016212108
- Radovčić D, Sršen AO, Radovčić J & Frayer DW 2015. Evidence for Neandertal Jewelry: Modified White-Tailed Eagle Claws at Krapina. PLoS ONE 10(3): e0119802, 1–14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119802
- Reilly PF, Tjahjadi A, Miller SL, Akey JM & Tucci S 2022. The contribution of Neanderthal introgression to modern human traits. Current Biology 32(18), R970–R983. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2022.08.027
- Rodríguez-Hidalgo A, Morales JI, Cebrià A et al. 2019. The Châtelperronian Neanderthals of Cova Foradada (Calafell, Spain) used imperial eagle phalanges for symbolic purposes. Science Advances 5(11): eaax1984, 1–11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aax1984
- Rodríguez-Vidal J, d’ Errico F, Pacheco FG et al. (2014). A rock engraving made by Neanderthals in Gibraltar. PNAS 111(37), 13301–13306. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1411529111
- Roebroeks W, Sier MJ, Kellberg Nielsen T, de Loecker D, Parés JM, Arps CES & Mücher HJ 2012. Use of red ochre by early Neandertals. PNAS 109(6), 1889–1894. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1112261109
- Schmidt P, Koch TJ, Blessing MA, Karakostis FA, Harvati K, Dresely V & Charrié-Duhaut A 2023. Production method of the Königsaue birch tar documents cumulative culture in Neanderthals. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences 15: 84, 1–13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-023-01789-2
- Seghers E 2018. A Tale of Two Species: The Origins of Art and the Neanderthal Challenge. Evolutionary Studies and Imaginative Culture 2(2), 83–102. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26613/esic.2.2.94
- Shermer M 2010. Our Neandertal Brethren: Why They Were Not a Separate Species. Scientific American 303(2), 34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/scientificamerican0810-34
- Soressi M, McPherron SP, Lenoir M et al. 2013. Neandertals made the first specialized bone tools in Europe. PNAS 110(35), 14186–14190. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1302730110
- Starr M 2021. In a Momentous Discovery, Scientists Show Neanderthals Could Produce Human-Like Speech. ScienceAlert March 1, 2021. https://www.sciencealert.com/neanderthals-could-both-hear-and-produce-human-like-speech
- Stringer C 2023. Are Neanderthals the same species as us? Natural History Museum 2023. https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/are-neanderthals-same-species-as-us.html
- Tattersall I & Schwartz JH 2006. The distinctiveness and systematic context of Homo neanderthalensis. pp. 9–22 in: Hublin J-J, Harvati K & Harrison T (eds). Neanderthals Revisited: New Approaches and Perspectives. Springer, Dordrecht (NL), xiv+332 pp. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4020-5121-0_2
- Turk M, Turk I, Dimkaroski L, Blackwell BAB, Horusitzky FZ, Otte M, Bastiani G & Korat L 2018. The Mousterian Musical Instrument from the Divje babe I cave (Slovenia): Arguments on the Material Evidence for Neanderthal Musical Behaviour. L’Anthropologie 122(4), 679–706. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anthro.2018.10.001
- Vernimmen T 2023. Neanderthals: More knowable now than ever. Knowable Magazine November 28, 2023. https://knowablemagazine.org/content/article/society/2023/new-finds-about-neanderthal-brains-and-behavior
- Villa P, Soriano S, Pollarolo L, Smriglio C, Gaeta M, d’Orazio M, Conforti J & Tozzi C 2020. Neandertals on the beach: Use of marine resources at Grotta dei Moscerini (Latium, Italy). PLoS ONE 15(1): e0226690, 1–35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal. pone.0226690
- Villanea FA & Schraiber JG 2019. Multiple episodes of interbreeding between Neanderthal and modern humans. Nature Ecology & Evolution 3, 39–44. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-018-0735-8
- Weyrich LS, Duchene S, Soubrier J et al. 2017. Neanderthal behaviour, diet, and disease inferred from ancient DNA in dental calculus. Nature 544(7650), 357–361. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21674
- Wolpoff M & Caspari R 1996. An Unparalleled Parallelism. Anthropologie 34(3), 215–223. https://www.jstor.org/stable/44601502
- Wynn T, Overmann KA & Coolidge FL 2016. The false dichotomy: a refutation of the Neandertal indistinguishability claim. Journal of Anthropological Sciences 94, 201–221. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26708102/
