 Evolution
Evolution
 Paleontology
Paleontology
Fossil Friday: Protists Add to the Cambrian Explosion
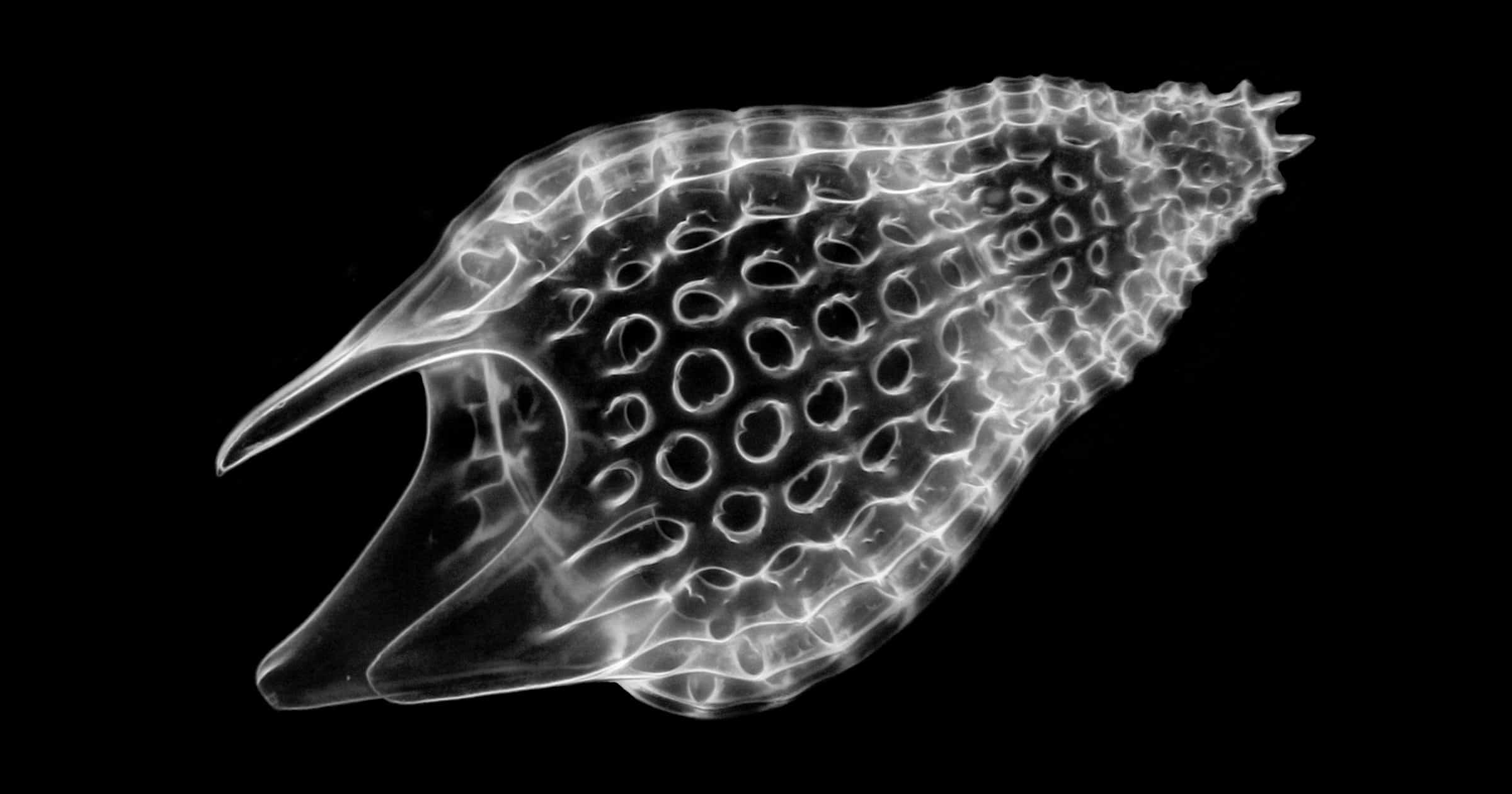
When talking about the Cambrian Explosion, the focus is usually on the abrupt appearance of bilaterian animal phyla with their distinct body plans, which has been called a Big Bang of life. However, the Cambrian Explosion is not restricted to these animals. As I have shown in previous articles, non-bilaterian animals like true sponges and jellyfish also first appeared in the Lower Cambrian (Bechly 2020, 2023). Today we will have a look at a largely ignored part of the Cambrian Explosion. That is the abrupt appearance of several major groups of protists (Lipps 1993, Wikipedia 2023).
Radiolarians represent an important group of marine zooplankton with beautiful siliceous mineral skeletons that were famously featured in wonderful drawings by the German pioneer Darwinist Ernst Haeckel. Their oldest fossil record is from the Earliest Cambrian (Ediacaran-Cambrian boundary) to Middle Cambrian of China (Braun et al. 2007, Maletz 2017, Chang et al. 2018, Zhang & Feng 2019, Zhang et al. 2021). Thus, they appear right together with the Cambrian Explosion of animal phyla.
Tentative Determinations
Foraminiferans are amoeboid marine protists, which mostly live in the seafloor sediment and have a calcium carbonate skeleton. Their oldest uncontroversial fossil record is again from the Early Cambrian (e.g., Culver 1991, McIlroy et al. 2001, Streng et al. 2005). Pawlowski et al. (2003) therefore concluded that “Fossil Foraminifera appear in the Early Cambrian, at about the same time as the first skeletonized metazoans.” More recent evidence for late Ediacaran foraminiferans suggests that this group may have originated already with the Avalon Explosion rather than the Cambrian Explosion (Gaucher & Sprechermann 1999, Hua et al. 2010, Pazio 2012, Chai et al. 2021), but even Hua et al. (2010) admitted that “the oldest unambiguous foraminifers are from Early Cambrian Atdabanian Stage strata.” Possible testate amoebae and possible foraminiferans (Rhizaria) have even been reported from 716-635 million-year-old carbonate rocks in Namibia and Mongolia, which date to a time right after the Sturtian glaciation of the Cryogenian “Snowball Earth” (Bosak et al. 2011, 2012, Parry 2011). However, these determinations are only tentative and far from established. At least the tintinnid determinations in the same work have been strongly disputed by Lipps et al. (2012) (see below).
Dinoflagellates are another important group of planktonic protists. Even though the oldest fossil dinoflagellates are known from middle Triassic sediments, there is indirect evidence from geochemical markers that these protists also first appeared in the Lower Cambrian period (Moldowan & Talyzina 1998).
“Darwin’s Dilemma Still Holds”
Other groups of protists appeared at other periods in Earth history, but they also originated abruptly without gradual transition from assumed precursors. For example, diatoms suddenly appear in the fossil record of the Early Jurassic about 182 million years ago (Kooistra & Medlin 1996, Bryłka et al. 2023). Coccolithophores (Hapotophyta), which form the chalk of the famous White Cliffs of Dover, appear at the Norian-Rhaetian boundary about 208.5 million years ago (Gardin et al. 2012). Uncontroversial tintinnids (Ciliata) are first recorded from Upper Triassic to Lower Cretaceous sediments, while several alleged Proterozoic records about 1.600-580 million years ago as well as Paleozoic records are all very doubtful and disputed (Lipps et al. 2012). Lipps et al. (2012) commented that “no solid evidence of Proterozoic tintinnids or other ciliates comes from the Precambrian rock record. Darwin’s dilemma of the lack of fossils for this ancient age (Schopf 2001; Knoll 2004) therefore still holds for at least the ciliates. If there are tintinnid fossils from this ancient time, they have yet to be discovered.”
Not even the tiniest and most abundant organisms seem to confirm the gradualist predictions of Darwinian evolution. Whenever empirical data from the actual fossil record are used to test this crucial part of the theory, it simply fails. Since gradualism is strongly refuted by the evidence, the theory must be false, because even Richard Dawkins, arguably the most ardent modern popularizer of Darwinism, clearly stated in his bestselling book The Greatest Show on Earth (Dawkins 2009) that “evolution not only is a gradual process as a matter of fact; it has to be gradual if it is to do any explanatory work.” Clinging to a refuted paradigm, in spite of the accumulated conflicting evidence, is not science but rather irrational dogmatic belief.
References
- Antcliffe JB, Gooday AJ & Brasier MD 2011. Testing the protozoan hypothesis for Ediacaran fossils: a developmental analysis of Palaeopascichnus. Palaeontology 54(5), 1157–1175. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-4983.2011.01058.x
- Bechly G 2020. The Myth of Precambrian Sponges. Evolution News May 12, 2020. https://evolutionnews.org/2020/05/the-myth-of-precambrian-sponges/
- Bechly G 2023. Fossil Friday: Jellyfish Body Plan and Life Cycle Originated in the Cambrian Explosion. Evolution News September 22, 2023. https://evolutionnews.org/2023/09/fossil-friday-jellyfish-body-plan-and-life-cycle-originated-in-the-cambrian-explosion/
- Bosak T, Lahr DJG, Pruss SB, Macdonald FA, Dalton L & Matys E 2011. Agglutinated tests in post-Sturtian cap carbonates of Namibia and Mongolia. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 308(1-2), 29–40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2011.05.030
- Bosak T, Lahr DJG, Pruss SB, Macdonald FA, Godday AJ, Dalton L & Matys ED 2012. Possible early foraminiferans in post-Sturtian (716−635 Ma) cap carbonates. Geology 40(1), 67–70. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1130/G32535.1
- Braun A, Chen J, Waloszek D & Maas A 2007. First Early Cambrian Radiolaria. pp. 143–149 in: Vickers-Rich P & Komarower P (eds). The Rise and Fall of the Ediacaran Biota. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 286(1). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1144/SP286.10
- Bryłka K, Alverson AJ, Pickering RA, Richoz S & Conley DJ 2023. Uncertainties surrounding the oldest fossil record of diatoms. Scientific Reports 13: 8047, 1–12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35078-8
- Chai S, Hua H, Ren J, Dai Q & Cui Z 2021. Vase-shaped microfossils from the Late Ediacaran Dengying Formation of Ningqiang, South China: taxonomy, taphonomy and biological affinity. Precambrian Research 352: 105968. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2020.105968
- Chang S, Feng Q & Zhang L 2018. New Siliceous Microfossils from the Terreneuvian Yanjiahe Formation, South China: The Possible Earliest Radiolarian Fossil Record. Journal of Earth Science 29(4), 912–919. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0960-0
- Culver SJ 1991. Early Cambrian foraminifera from West Africa. Science 254(5032), 689–691. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.254.5032.689
- Dawkins R 2009. The Greatest Show on Earth. Free Press, New York (NY), 470 pp.
- Gardin S, Krystyn L, Richoz S, Bartolini A & Galbrun B 2012: Where and when the earliest coccolithophores? Lethaia 45(4), 507–523. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1502-3931.2012.00311.x
- Gaucher C & Sprechermann P 1999. Upper Vendian skeletal fauna of the Arroyo del Soldado Group, Uruguay. Beringeria 23, 55–91. https://www.academia.edu/24415657/Upper_Vendian_skeletal_fauna_of_the_Arroyo_del_Soldado_Group_Uruguay
- Hua H, Chen Z, Yuan XL, Xiao SH & Cai YP 2010. The earliest Foraminifera from southern Shaanxi, China. Science China Earth Sciences 53(12), 1756–1764. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-010-4085-x
- Kooistra WHCF & Medlin LK 1996. Evolution of the Diatoms (Bacillariophyta). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 6(3), 391–407. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.1996.0088
- Lipps JH 1993. Fossil Prokaryotes and Protists. Blackwell: Cambridge (MA), x+342 pp.
- Lipps JH, Stoeck T & Dunthorn M 2012. Fossil tintinnids. Chapter 8, pp. 186–197 in: Dolan JR, Montagnes DJS, Agatha S, Wayne Coats D & Stoecker DK (eds). The Biology and Ecology of Tintinnid Ciliates: Models for Marine Plankton. John Wiley & Sons: Chichester (UK), viii+296 pp. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118358092.ch8
- Maletz J 2017. The identification of putative Lower Cambrian Radiolaria. Revue de Micropaléontologie 60(2), 233–240. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.revmic.2017.04.001
- McIlroy D, Green OR & Brasier MD 2001. Paleobiology and evolution of the earliest agglutinated Foraminifera: Platysolenites, Spirosolenites and related forms. Lethaia 34(1), 13–29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/002411601300068170
- Moldowan JM & Talyzina NM 1998. Biogeochemical evidence for dinoflagellate ancestors in the Early Cambrian. Science 281(5380), 1168–1170. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.281.5380.1168
- Parry W 2011. Oldest Hairy Microbe Fossils Discovered. LiveScience November 26, 2011. https://www.livescience.com/17182-oldest-hairy-microbes-discovered.html
- Pawlowski J, Holzmann M, Berney C, Fahrni J, Gooday AJ, Cedhagen T, Habura A & Bowser SS 2003. The evolution of early Foraminifera. PNAS 100(20), 11494–11498. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2035132100
- Pazio M 2012. The late Ediacaran Agglutinated Foraminifera from Finnmark, Northern Norway. University Uppsala Självständigt arbete i geovetenskap 43, 1–46. https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:565246/FULLTEXT01.pdf
- Streng M, Babcock LE & Hollingsworth JS 2005. Agglutinated protists from the Lower Cambrian Nevada. Journal of Paleontology 79(6), 1214–1218. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1666/0022-3360(2005)079[1214:APFTLC]2.0.CO;2
- Wikipedia 2023. Protists in the fossil record. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protists_in_the_fossil_record
- Zhang K & Feng Q-L 2019. Early Cambrian radiolarians and sponge spicules from the Niujiaohe Formation in South China. Palaeoworld 28(3), 234–242. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palwor.2019.04.001
- Zhang Y, Feng Q, Nakamura Y & Suzuki N 2021. Microfossils from the Liuchapo Formation: Possible oldest radiolarians from deep-water chert and phylogenetic analysis. Precambrian Research 362: 106312, 1–11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2021.106312
